ESG Scores and Rising Debt Costs: An Emerging Opportunity for Libya
By Julio Alonso
This article critically examines the nexus between Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) scores and the cost of debt, with a pivotal focus on discerning emerging opportunities within the global energy landscape. As the realms of ESG continue to wield significant influence on investment and financing decisions, complex dynamics underpinning markets such as fossil fuels manifesting palpable impacts on their respective value chains. In navigating through the seasonal and geopolitical fluctuations in energy markets, this text unveils the potential avenues through which Libya, laden with access to inexpensive capital and substantial foreign assets, could strategically leverage these prevailing conditions to foster economic rejuvenation.
Table of Contents
ESG Scores’ Impact on Investment and Borrowing
In recent years, investors have been intensifying their focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors, recognizing them as pivotal determinants in evaluating a company’s long-term value and ethical impact, particularly within sectors like energy. Governed by frameworks such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals, ESG metrics encompass various considerations, including environmental impacts and adherence to sustainable practices.
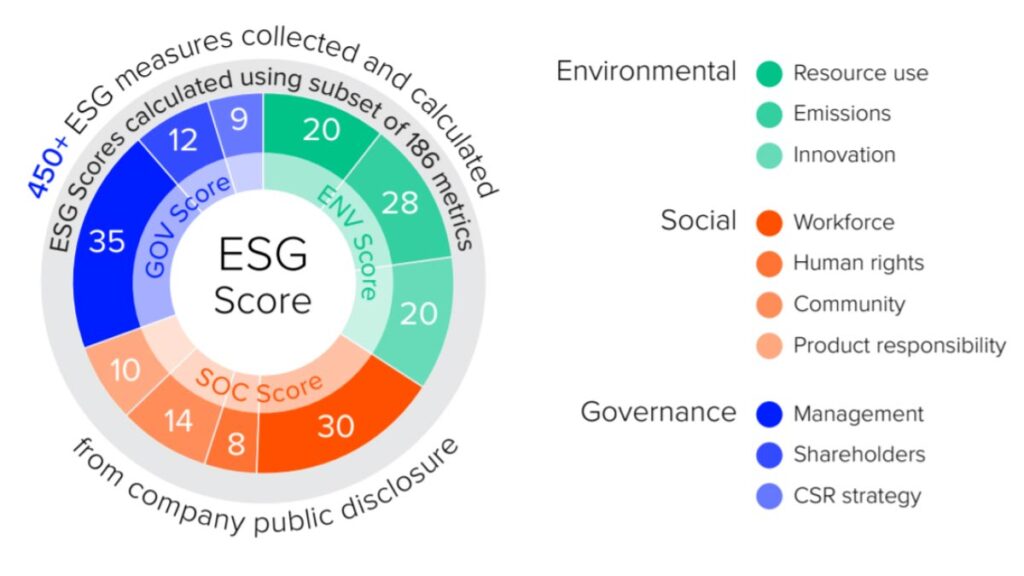
High ESG scores signal a company’s resilience against multifarious risks such as environmental, legal, and operational, portraying them as judicious investment avenues with reduced potential liabilities. Market trends substantiate a remarkable ascendance of ESG assets, projected to eclipse $50 trillion by 2025, reflecting a seismic shift towards sustainable investing.
However, suboptimal ESG adherence manifests in escalated borrowing costs due to market apprehension towards inherent risks and liabilities, thus engendering a recalibration of conventional financial metrics through a sustainability lens, creating suboptimal capital allocations that permeate market efficiency. This dynamic reshaping of worldwide capital allocation underscores the indelible influence of ESG considerations in contemporary investment paradigms, signifying a transformative shift in global investment strategies and frameworks.
How Do ESG-Linked Loans Work?
In the midst of this discourse a key aspect are ESG-linked loans, which are revolutionizing traditional lending paradigms by integrating sustainability metrics into loan pricing strategies. Unlike conventional loans, which primarily rely on benchmarks like Euribor or SOFR, and variables such as credit ratings and deal length, ESG-linked loans introduce sustainability performance as a pivotal determinant in loan cost structures. Borrowers’ adherence to specific ESG targets or key performance indicators (KPIs), such as carbon footprint reduction or gender diversity enhancement, influences the loan’s interest rate, either as a discount or a penalty.

In scenarios where corporate facilities remain undrawn, sustainability-pricing adjustments are applied to commitment fees, reflecting a nuanced approach towards incentivizing ESG compliance. This strategy amplifies the role of ESG as a crucial risk factor, shaping the investment appetite of international funds and nations by recalibrating support towards industries aligning with sustainability objectives.
ESG-linked loans, therefore, emerge as strategic conduits that foster a synergy between financial robustness and sustainability commitments, redefining investment and borrowing landscapes in alignment with evolving global sustainability imperatives.
Is ESG a New Risk Factor?
Such an imperative position of ESG in the economic field causes for new findings. Recent research by Amundi Asset Management offers insights using single-factor and multi-factor models, employing various standard factors like size, value, and momentum within a factor investing framework. Using weekly return analyses, the research evaluates the influence of each factor on stock returns. ESG has emerged as a significant factor, particularly competitive against market risk. For instance, in the Eurozone, the ESG factor explained about 35.3% of the cross-sectional variance from 2014 to 2019, which is quite close to the 36.3% explained by the market risk factor.
Comparing different models, introducing ESG as a factor did not notably enhance the explanatory power of the traditional five-factor model. Its significance varied geographically; it emerged as a statistically significant risk factor in the Eurozone, unlike in North America.
More importantly, ESG’s role extends beyond assessing companies’ capital access, influencing global investment funds and nations in their association with industries and projects scoring low on ESG. In conclusion, the ESG factor’s relevance appears more pronounced in the Eurozone, shaping investment strategies and affiliations with lower-scoring ESG entities.
The Case of Coal and Diesel
Despite a strong popularity in the Eurozone, the ESG ratings have not had the best effects in specific industries and countries. The intersection of strict ESG requirements and geopolitical upheavals has pushed sectors like coal and diesel into a challenging environment characterized by rising financial expenses and significant obstacles to starting new projects.
In the diesel realm, critical market inefficiencies loom, exemplified by a stark 1.5% reduction in global refinery production this quarter, culminating in a daily shortfall of approximately 1.2 million barrels. Compounded by OPEC+ output contractions and geopolitical contention, the industry grapples with a dire scarcity, endangering supply chains as burgeoning demand shadows the northern winter.
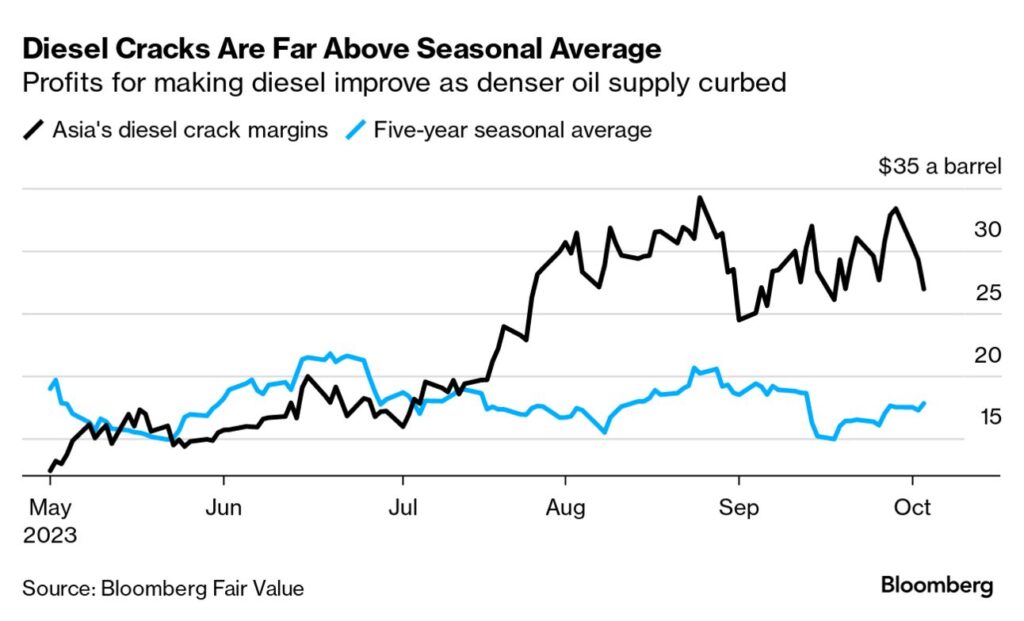
Concurrently, the coal industry navigates a labyrinth of investment restrictions and diminished project viability. Prevailing ESG strictures have orchestrated a discernible contraction in new enterprise inceptions, particularly within OECD territories, despite resilient demand currents in emerging markets. A landscape marred by project cancellations and receding stock valuations heralds an uncertain future, echoing the hardships endured by this transformative energy sector.
This turbulent intersection of variables casts a long shadow of uncertainty and hardship over these non-ESG compliant sectors, reverberating with pronounced negative impacts across supply chains and market efficiencies. The current circumstances highlight a path filled with difficulties, indicating a prolonged phase of adaptation and the need for strategic reevaluation in light of ongoing challenges.
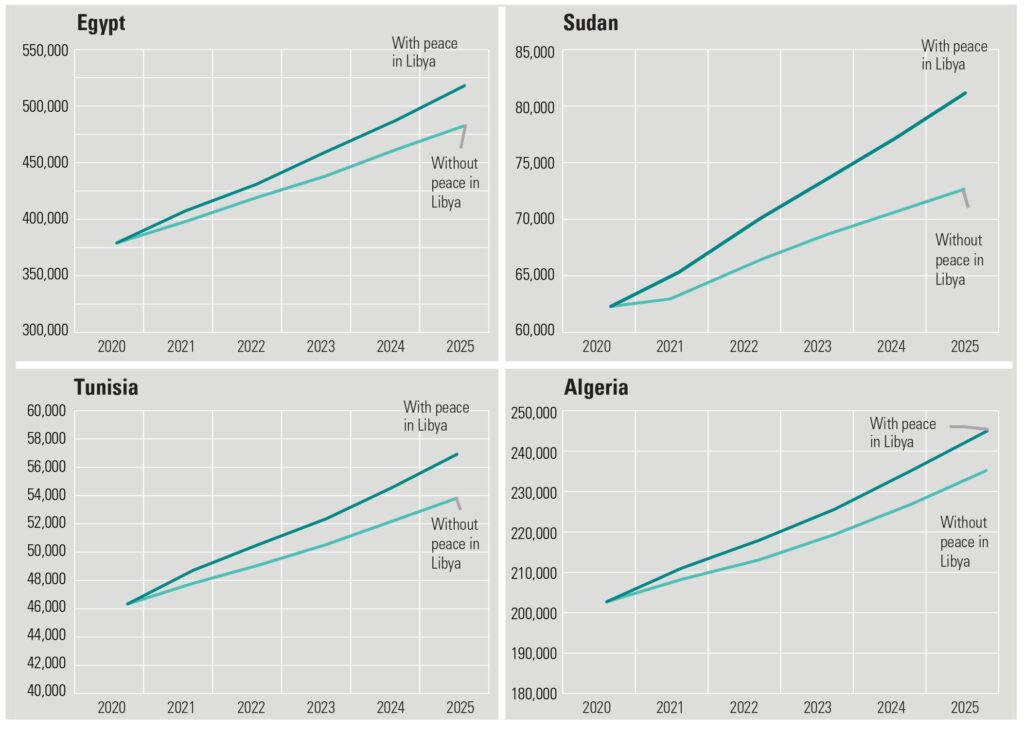
Libya, the Global South & East
As we examine the challenging landscape faced by coal and diesel industries in the context of ESG mandates and geopolitical turbulence, our attention should shift to regions like Libya and the Global South and East. These areas, with their distinctive investment considerations and less stringent ESG constraints, provide a different perspective on this evolving environment.
In the current shifting energy investment landscape, the Global South and East emerge as resilient arenas for low-score ESG initiatives, navigating practical needs and infrastructural realities. They present diverse investment considerations, unencumbered by the stringent ESG constraints predominant in Western economies. Libya, uniquely positioned within this paradigm, stands out with strategic advantages such as accessible capital and a strong asset base, enabling optimized investment decisions amidst dynamic ESG and geopolitical considerations.

Political transitions and changing attitudes towards nations sanctioned based on Environmental, Social, and Governance factors, as evidenced in the Biden administration easing of sanctions on Venezuela’s oil sector earlier this week, further nuance this trajectory.
In conclusion, Libya embodies significant potential to adeptly maneuver through prevailing global energy market conditions, leveraging accessible capital and substantial foreign assets towards economic rejuvenation and strategic progression within the comprehensive energy landscape. Its role is pivotal in recalibrating investment pathways, harnessing the intersection of ESG, geopolitical shifts, and market variables to optimize investment outcomes in the contemporary energy architecture.